News
Stoma classification:
Release time:2022-04-15
Clinically, according to the different lesions and surgical sites, stoma can be divided into:
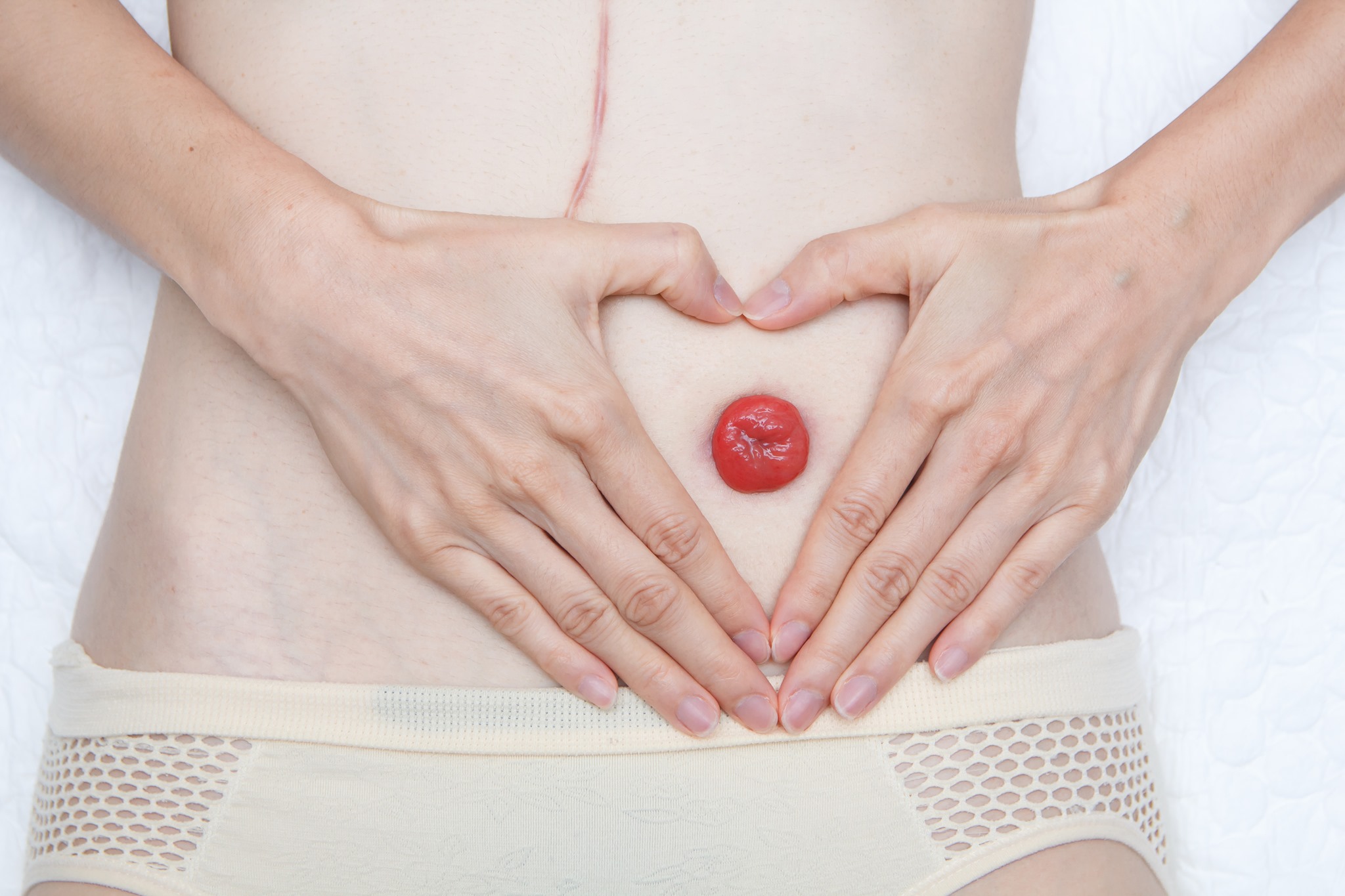
- Colostomy
With 1- 1.5 cm higher than the abdominal wall and a diameter about 3 – 5 cm, the colostomy is usually located at left hypogastrium, and is a permanent stoma for the colon or sigmoid. The feces excreted from here is usually shaped.
- Ileostomy
With 1.5- 2.5 cm higher than the abdominal wall and a diameter about 2- 2.5 cm, the ileostomy is usually located at the right hypogastrium, and is the opening of the distal ileum in the abdominal wall. The feces excreted from here is usually liquid and rich in digestive enzymes causing strong thrill to the surrounding skin.
- Temporary Stoma
The stoma is located in transverse colon segment, that is, the epigastrium, and is double-barrel or loop stoma with large appearance. The proximal stoma excretes loose stool, while the distal stoma excretes only a small amount of intestinal mucus. Temporary stoma plays the role of shunt and decompression, which can be closed when the diseases of the lower segment of the intestinal heal.
- Urostomy
The urostomy is usually located at the right hypogastrium, but sometimes can be determined by the doctor according to the actual situation of surgery. Use a segment of the free ileum to replace the bladder. With 2-3 cm higher than abdominal wall and a diameter of about 2 – 2.5 cm, the stoma is located at abdominal wall. After surgery, urine is discharged through this stoma.